Report:
California’s Middle-Class Wages Rise by 1 Percent in 40 Years
Justin Sullivan/Getty Images
3 Sep 2019172
6:24
Middle-class
wages in progressive California have risen by 1 percent in the last 40 years,
says a study by the establishment California Budget and Policy Center.
“Earnings for California’s
workers at the low end and middle of the wage scale have generally declined or
stagnated for decades,” says the report, titled “California’s Workers Are
Increasingly Locked Out of the State’s Prosperity.” The report continued:
In
2018, the median hourly earnings for workers ages 25 to 64 was $21.79, just 1%
higher than in 1979, after adjusting for inflation ($21.50, in 2018 dollars)
(Figure 1). Inflation-adjusted hourly earnings for low-wage workers, those at the
10th percentile, increased only slightly more, by 4%, from $10.71 in 1979
to $11.12 in 2018.
The report admits that the
state’s progressive economy is delivering more to investors and less to
wage-earners. “Since 2001, the share of state private-sector [annual new
income] that has gone to worker compensation has fallen by 5.6 percentage
points — from 52.9% to 47.3%.”
In 2016, California’s Gross
Domestic Product was $2.6 trillion, so the 5.6 percent drop shifted $146
billion away from wages. That is roughly $3,625 per person in 2016.
The report notes that wages
finally exceeded 1979 levels around 2017, and it splits the credit between the
Democrats’ minimum-wage boosts and President Donald Trump’s go-go economy.
The 40 years of flat wages are
partly hidden by a wave of new products and services. They include almost-free
entertainment and information on the Internet, cheap imported coffee in
supermarkets, and reliable, low-pollution autos in garages.
But the impact of California’s
flat wages is made worse by California’s rising housing costs, the report says,
even though it also ignores the rent-spiking impact of the establishment’s
pro-immigration policies:
In just the last decade
alone, the increase in the typical household’s rent far outpaced the rise in
the typical full-time worker’s annual earnings, suggesting that working
families and individuals are finding it increasingly difficult to make ends
meet. In fact, the basic cost of living in many parts of the state is more
than many single individuals or families can expect to earn, even if all adults
are working full-time.
…
Specifically, inflation-adjusted
median household rent rose by 16% between 2006 and 2017, while
inflation-adjusted median annual earnings for individuals working at least 35
hours per week and 50 weeks per year rose by just 2%, according to a Budget
Center analysis of US Census Bureau, American Community Survey data.
Many workers are being paid
little more today than workers were in 1979 even as worker productivity has
risen. Fewer employees have access to retirement plans sponsored by their
employers, leaving individual workers on their own to stretch limited dollars
and resources to plan how they’ll spend their later years affording the high
cost of living and health care in California. And as union representation has
declined, most workers today cannot negotiate collectively for better working
conditions, higher pay, and benefits, such as retirement and health care, like
their parents and grandparents did. On top of all this, workers who take on
contingent and independent work (often referred to as “gig work”), which in
many cases appears to be motivated by the need to supplement their primary job
or fill gaps in their employment, are rarely granted the same rights and legal
protections as traditional employees.
The center’s report tries to
blame the four-decade stretch of flat wages on the declining clout of unions.
But unions’ decline was impacted by the bipartisan elites’ policy of
mass-migration and imposed diversity.
In
2018, Breitbart reported how
Progressives for Immigration Reform interviewed Blaine Taylor, a union
carpenter, about the economic impact of migration:
TAYLOR: If I hired a framer to do
a small addition [in 1988], his wage would have been $45 an hour. That was
the minimum for a framing contractor, a good carpenter. For a helper, it was
about $25 an hour, for a master who could run a complete job, it was about $45
an hour. That was the going wage for plumbers as well. His helpers typically
got $25 an hour.
…
Now, the average wage in Los
Angeles for construction workers is less than $11 an hour. They can’t go lower
than the minimum wage. And much of that, if they’re not being paid by the hour
at less than $11 an hour, they’re being paid per piece — per piece of plywood
that’s installed, per piece of drywall that’s installed. Now, the subcontractor
can circumvent paying them as an hourly wage and are now being paid by 1099,
which means that no taxes are being taken out. [Emphasis added]
Diversity
also damaged the unions by shredding California’s civic solidarity. In 2007,
the progressive Southern Poverty Law Center posted a
report with the title “Latino Gang Members in Southern California are
Terrorizing and Killing Blacks.” In the same year, an op-ed in the Los Angeles Times described another
murder by Latino gangs as “a manifestation of an increasingly common
trend: Latino ethnic cleansing of African Americans from multiracial
neighborhoods.”
The center’s board members
include the executive director of the state’s SEIU union, a professor from the
Goldman School of Public Policy at the University of California, Berkeley, and
the research director at the “Program for Environmental and Regional Equity” at
the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Outside
California, President Donald Trump’s low-immigration policies are pressuring
employers to raise Americans’ wages in a hot economy. The Wall Street Journal reportedAugust
29:
Overall, median weekly earnings
rose 5% from the fourth quarter of 2017 to the same quarter in 2018, according
to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. For workers between the ages of 25 and 34,
that increase was 7.6%.
HOME TO
DIANNE FEINSTEIN, NANCY PELOSI, KAMALA HARRIS AND GAVIN NEWSOM
Adios,
Sanctuary La Raza Welfare State of California
A fifth-generation Californian laments his state’s ongoing economic collapse.
By Steve Baldwin
American Spectator
What’s clear is that the producers are leaving the state and the takers are coming in. Many of the takers are illegal aliens, now estimated to number over 2.6 million (BLOG: THE NUMBER IS CLOSER TO 15 MILLION ILLEAGLS). The Federation for American Immigration Reform estimates that California spends $22 billion (DATED: NOW ABOUT $35 BILLION YEARLY AND THAT IS ON THE STATE LEVEL ONLY. COUNTIES PAY OUT MORE) on government services for illegal aliens, including welfare, education, Medicaid, and criminal justice system costs.
A fifth-generation Californian laments his state’s ongoing economic collapse.
By Steve Baldwin
American Spectator
What’s clear is that the producers are leaving the state and the takers are coming in. Many of the takers are illegal aliens, now estimated to number over 2.6 million (BLOG: THE NUMBER IS CLOSER TO 15 MILLION ILLEAGLS). The Federation for American Immigration Reform estimates that California spends $22 billion (DATED: NOW ABOUT $35 BILLION YEARLY AND THAT IS ON THE STATE LEVEL ONLY. COUNTIES PAY OUT MORE) on government services for illegal aliens, including welfare, education, Medicaid, and criminal justice system costs.
Liberals
claim they more than make that up with taxes paid, but that’s simply not true.
It’s not even close. FAIR estimates illegal aliens in California contribute
only $1.21 billion in tax revenue, which means they cost California $20.6
billion, or at least $1,800 per household.
Nonetheless, open border advocates, such as Facebook Chairman Mark Zuckerberg, claim illegal aliens are a net benefit to California with little evidence to support such an assertion. As the Center for Immigration Studies has documented, the vast majority of illegals are poor, uneducated, and with few skills. How does accepting millions of illegal aliens and then granting them access to dozens of welfare programs benefit California’s economy? If illegal aliens were contributing to the economy in any meaningful way, California, with its 2.6 million illegal aliens, would be booming.
Furthermore, the complexion of illegal aliens has changed with far more on welfare and committing crimes than those who entered the country in the 1980s. Heather Mac Donald of the Manhattan Institute has testified before a Congressional committee that in 2004, 95% of all outstanding warrants for murder in Los Angeles were for illegal aliens; in 2000, 23% of all Los Angeles County jail inmates were illegal aliens and that in 1995, 60% of Los Angeles’s largest street gang, the 18th Street gang, were illegal aliens. Granted, those statistics are old, but if you talk to any California law enforcement officer, they will tell you it’s much worse today. The problem is that the Brown administration will not release any statewide data on illegal alien crimes. That would be insensitive. And now that California has declared itself a “sanctuary state,” there is little doubt this sends a message south of the border that will further escalate illegal immigration into the state.
Nonetheless, open border advocates, such as Facebook Chairman Mark Zuckerberg, claim illegal aliens are a net benefit to California with little evidence to support such an assertion. As the Center for Immigration Studies has documented, the vast majority of illegals are poor, uneducated, and with few skills. How does accepting millions of illegal aliens and then granting them access to dozens of welfare programs benefit California’s economy? If illegal aliens were contributing to the economy in any meaningful way, California, with its 2.6 million illegal aliens, would be booming.
Furthermore, the complexion of illegal aliens has changed with far more on welfare and committing crimes than those who entered the country in the 1980s. Heather Mac Donald of the Manhattan Institute has testified before a Congressional committee that in 2004, 95% of all outstanding warrants for murder in Los Angeles were for illegal aliens; in 2000, 23% of all Los Angeles County jail inmates were illegal aliens and that in 1995, 60% of Los Angeles’s largest street gang, the 18th Street gang, were illegal aliens. Granted, those statistics are old, but if you talk to any California law enforcement officer, they will tell you it’s much worse today. The problem is that the Brown administration will not release any statewide data on illegal alien crimes. That would be insensitive. And now that California has declared itself a “sanctuary state,” there is little doubt this sends a message south of the border that will further escalate illegal immigration into the state.
"If the racist "Sensenbrenner Legislation" passes the US
Senate, there is no doubt that a massive civil disobedience movement will
emerge. Eventually labor union power can merge with the immigrant civil rights
and "Immigrant Sanctuary" movements to enable us to either
form a new political party or to do heavy duty reforming of the existing
Democratic Party. The next and final steps would follow and that is to elect
our own governors of all the states within Aztlan."
Indeed, California goes out of its way to attract illegal aliens. The state has even created government programs that cater exclusively to illegal aliens. For example, the State Department of Motor Vehicles has offices that only process driver licenses for illegal aliens. With over a million illegal aliens now driving in California, the state felt compelled to help them avoid the long lines the rest of us must endure at the DMV. And just recently, the state-funded University of California system announced it will spend $27 million on financial aid for illegal aliens. They’ve even taken out radio spots on stations all along the border, just to make sure other potential illegal border crossers hear about this program. I can’t afford college education for all my four sons, but my taxes will pay for illegals to get a college education.
Indeed, California goes out of its way to attract illegal aliens. The state has even created government programs that cater exclusively to illegal aliens. For example, the State Department of Motor Vehicles has offices that only process driver licenses for illegal aliens. With over a million illegal aliens now driving in California, the state felt compelled to help them avoid the long lines the rest of us must endure at the DMV. And just recently, the state-funded University of California system announced it will spend $27 million on financial aid for illegal aliens. They’ve even taken out radio spots on stations all along the border, just to make sure other potential illegal border crossers hear about this program. I can’t afford college education for all my four sons, but my taxes will pay for illegals to get a college education.
CBO: Immigration Has ‘Negative Effect on Wages’

7:01
Immigration makes all of America richer, but it can make some Americans poorer, the non-partisan Congressional Budget Office says in a report issued January 9.
“Immigration, whether legal or illegal, expands the labor force and changes its composition, leading to increases in total economic output,” said the non-partisan report, titled “The Foreign-Born Population and Its Effects on the U.S. Economy and the Federal Budget—An Overview.”
But this national expansion does “not necessarily [deliver] to increases in output per capita,” or income per person, the report said:
For example, business leaders say the nation’s enormous population of immigrants has expanded the nation’s workforce, increased consumption, and driven up housing prices. But that inflow has also shrunk the wages of less-educated Americans, the report said:
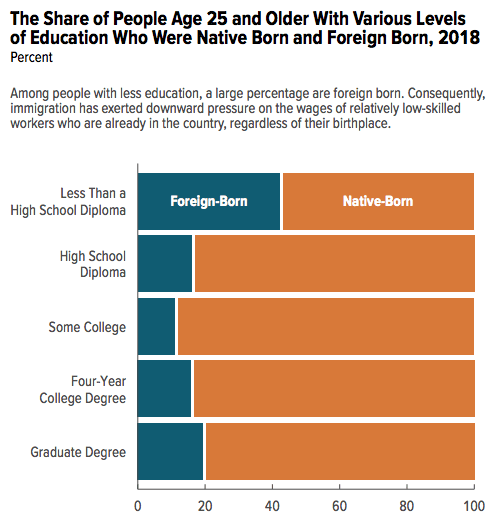
Among people with less education, a large percentage are foreign born. Consequently, immigration has exerted downward pressure on the wages of relatively low-skilled workers who are already in the country, regardless of their birthplace.
The CBO report contradicts business claims that a bigger economy ensures bigger wages for everyone.
More ominously, the report also suggests that the American middle-class — including millions of young college graduates — may suffer a similar economic disaster if immigration policy is shifted to raise the inflow of foreign college graduates. The report says:
The effects of immigration on wages depend on the characteristics of the immigrants. To the extent that newly arrived workers have abilities similar to those of workers already in the country, immigration would have a negative effect on wages.
Many business advocates in Washington are calling for a dramatic increase in “high-skilled immigration” — meaning foreign college graduates who would compete for the same jobs as American college graduates. For example, Sen. Mike Lee (R-UT) is trying to pass his S.386 bill that offers the prize of renewable work-permits — and eventual citizenship — to an unlimited number of foreign graduates.
Each year, up to 120,000 foreign graduates — and their spouses and children — can get green cards via their employer’s sponsorship, even as perhaps 800,000 Americans graduate from college with skilled degrees.
But Lee’s bill creates a new legal status called “Early Adjustment.” This status would allow an uncapped number of college graduate migrants to apply for renewable work permits long before they can get a green card to become a legal immigrant and citizen.
Existing law allows an uncapped number of foreigners to legally get short-term work permits and jobs after enrolling in U.S. colleges. The migrants can get jobs by first paying tuition to a university, and then getting short-term work permits via the uncapped “Curricular Practical Training” and the “Optional Practical Training” programs. These workers must leave the United States after a few years until they enroll themselves in work permit programs.
But Lee’s bill would remove any caps on this foreign worker population by allowing an unlimited number of foreign workers to get “Early Adjustment” status from their employers.
DHS posts videos of Indian migrants buying fake documents from ICE's Farmington U. sting operation.
The #OPT Optional Practical Training program is an estb.-run labor-trafficking scheme to sideline American graduates.
It will expand if #S386 becomes law bit.ly/39H2Zqh
Many migrants already use the CPT and OPT work permits to get jobs and to also compete for entry into the H-1B visa worker program. Once in the H-1B program — which accepts 85,000 new workers each year — many of the migrants also ask their employers to sponsor them for green cards.
The sponsorship allows them to stay working in the United States until they eventually get their valuable green card, long after their temporary visas have expired. Congress has not set an annual limit on the number of visa workers who can be sponsored for green cards, so the resident population of permanent “temporary workers” is growing fast — and is helping to suppress wages for American graduates.
Roughly 1.5 million foreign visa workers hold white-collar jobs throughout the U.S. economy. This number includes at least 750,000 Indians who are allowed to work via the supposedly temporary CPT, OPT, L-1, and H-1B visa programs. Roughly 300,000 of these Indians — plus 300,000 family members — are being allowed to stay in the United States because they asked their employers to sponsor them for green cards.
The CBO report shows that immigrants comprise roughly 40 percent of the population of people who did not graduate from high school — and that immigrants already comprise roughly 20 percent of all people with a “graduate degree.”
The 20 percent share likely would quickly rise if the Senate approves Lee’s S.386 plan — and that rise could sharply reduce salaries for American college graduates.
“Wage trends over the past half-century suggest that a 10 percent increase in the number of workers with a particular set of skills probably lowers the wage of that group by at least 3 percent” as the extra workers compete for jobs, says George Borjas, a labor economist at Harvard. That extra labor does expand the economy — but that expansion is dwarfed by the transfer of the wage reductions to investors, he wrote in 2016:
I estimate the current “immigration surplus”—the net increase in the total wealth of the native population—to be about $50 billion annually. But behind that calculation is a much larger shift from one group of Americans to another: The total wealth redistribution from the native losers to the native winners [mostly employers] is enormous, roughly a half-trillion dollars a year.
“In low-skilled occupations, a one percent increase in the immigrant composition of an individual’s occupation reduces wages by [0].8 percent,” said a 1998 report by the Center for Immigration Studies.
A 2013 CBO report predicted that the 2013 “Gang of Eight” amnesty and immigration bill would reduce the share of income that goes to wage earners and increase the share that goes to investors. “Because the bill would increase the rate of growth of the labor force, average wages would be held down in the first decade after enactment,” the CBO report said.
But all that cheap labor would boost corporate profits and spike the stock market, the report said. “The rate of return on capital would be higher [than on labor] under the legislation than under current law throughout the next two decades,” says the report, titled “The Economic Impact of S. 744.”
Business leaders sometimes admit that an extra supply of workers forces down wages. “If you have ten people for every job, you’re not going to have a drive [up] in wages,” U.S. Chamber of Commerce CEO Tom Donohue told Breitbart News on January 9. But “if you have five people for every ten jobs, wages are going to go up.”
Are rising wages good for national politics?
“You’re damn right they are,” US Chamber of Commerce CEO Tom Donohue said, adding: "They are good for national politics if you’re a politician, for sure."bit.ly/2FwwCg7


No comments:
Post a Comment